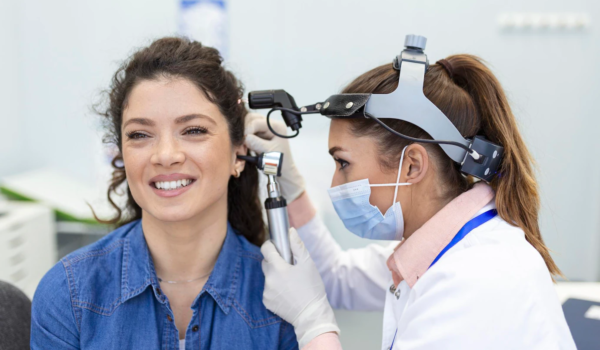
Welcome to the in-depth exploration of “Ear Infection Through Otoscope.” In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of ear infections, examining their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, all through the lens of an otoscope. Get ready to gain profound insights into this common ailment affecting millions of individuals worldwide.
Understanding Ear Infections
What is an Ear Infection?
Ear infections, medically known as otitis media, occur when the middle ear becomes inflamed and infected. They can be painful and affect people of all ages, but they are particularly prevalent in children.
Types of Ear Infections
- Acute Otitis Media: This is the most common type, characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms, including ear pain and fever;
- Chronic Otitis Media : This type persists for an extended period and may lead to hearing loss if left untreated;
- Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear): This infection affects the ear canal and is often caused by water exposure.
The Role of the Otoscope
What is an Otoscope?
An otoscope is a specialized medical device used by healthcare professionals to examine the inside of the ear. It consists of a light source and a magnifying lens, allowing for a detailed view of the ear canal and eardrum.
Importance of Otoscope in Diagnosis
The otoscope plays a crucial role in diagnosing ear infections by enabling healthcare providers to:
- Visualize the Ear Canal: The otoscope helps identify redness, swelling, and the presence of pus or fluid;
- Assess the Eardrum: It allows for the evaluation of the eardrum’s condition, which can indicate the severity of the infection.
Symptoms of Ear Infections
Recognizing the Signs
Ear infections often exhibit a range of symptoms, which may include:
- Ear Pain: A sharp or dull ache in the ear, especially when lying down;
- Fever: Particularly in cases of acute otitis media;
- Hearing Loss: Temporary or permanent, depending on the infection’s duration;
- Fluid Drainage: Pus or clear fluid may leak from the ear;
- Irritability: Especially in infants and young children.
Diagnosis and Otoscope Examination
The Otoscope Examination Process
- Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, and the otoscope is sanitized to prevent cross-contamination;
- Insertion: The healthcare provider gently inserts the otoscope into the ear canal, taking care not to cause discomfort;
- Visual Examination: Using the otoscope’s light and magnification, the healthcare provider assesses the ear canal and eardrum;
- Diagnosis: Based on the findings, a diagnosis is made, and the appropriate treatment plan is recommended.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early detection of ear infections through otoscope examination is crucial as it allows for prompt treatment, reducing the risk of complications such as hearing loss and chronic infections.
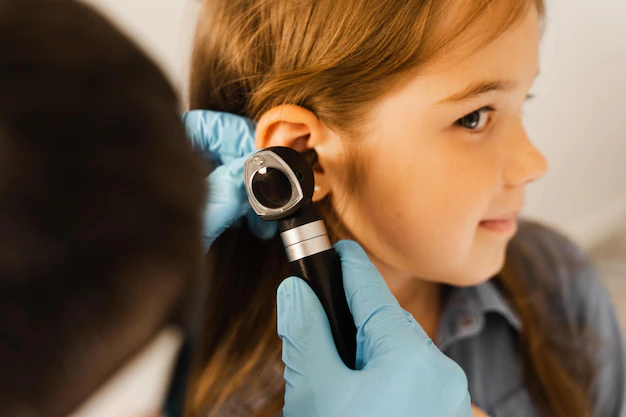
Treating Ear Infections
Conservative Management
In some cases, ear infections may resolve on their own without the need for antibiotics. This approach includes:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate discomfort;
- Warm Compresses: Applied to the affected ear for pain relief.
Antibiotics
When bacterial infections are identified, antibiotics may be prescribed. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is entirely eradicated.
Surgical Intervention
Severe or chronic ear infections may require surgical intervention, such as:
- Myringotomy: A procedure to drain fluid from the middle ear;
- Tympanoplasty: Repairing a perforated eardrum.
Prevention and Ear Health
Tips for Preventing Ear Infections
- Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with recommended vaccines, as some protect against infections that can lead to ear problems;
- Avoid Smoking: Exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of ear infections, especially in children;
- Proper Ear Hygiene: Avoid inserting foreign objects into the ear canal and keep ears dry after swimming.
Risk Factors for Ear Infections
Identifying Common Risk Factors
Ear infections can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing them. Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Children, especially those under 3 years old, are more susceptible. |
| Exposure to Smoke | Living with smokers or exposure to secondhand smoke can increase risk. |
| Seasonal Factors | Infections are more prevalent during the fall and winter months. |
| Daycare Attendance | Children in daycare settings may be more exposed to germs. |
| Allergies | Allergies can lead to ear congestion and increase the risk. |
| Family History | A family history of ear infections can predispose individuals. |
Home Remedies for Ear Pain Relief
Soothing Ear Pain at Home
While professional medical guidance is essential for treating ear infections, some home remedies can help alleviate ear pain:
| Home Remedy | Description |
|---|---|
| Warm Compress | Applying a warm, damp cloth to the ear can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. |
| Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers | Non-prescription pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with discomfort. |
| Hydration | Staying well-hydrated can prevent ear congestion and promote healing. |
| Rest and Elevation | Resting with the affected ear elevated can reduce pressure and discomfort. |
| Avoiding Irritants | Avoid exposing the ear to irritants like smoke or excessive noise. |
Ear Infections in Adults
Addressing Ear Infections in Adulthood
While ear infections are commonly associated with children, adults can also experience them. Here’s what you need to know:
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| Causes | Adult ear infections can result from factors like respiratory infections or Eustachian tube dysfunction. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms in adults may include ear pain, hearing loss, and fluid drainage. |
| Treatment | Treatment typically involves antibiotics or addressing the underlying cause. |
| Complications | Untreated infections can lead to more severe complications in adults. |
Preventing Recurrent Ear Infections
Strategies to Prevent Recurrence
For individuals prone to recurrent ear infections, these strategies can help reduce the frequency:
| Prevention Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Allergy Management | Managing allergies through medication or lifestyle changes can prevent ear congestion. |
| Hand Hygiene | Regular handwashing can reduce the risk of infection transmission. |
| Vaccination | Staying up-to-date with vaccinations, including the flu shot, can prevent some infections. |
| Ear Protection | Wearing earplugs or earmuffs in noisy or polluted environments can help protect your ears. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing When Medical Help Is Necessary
Ear infections often require medical evaluation and treatment. Here are signs that indicate it’s time to consult a healthcare professional:
- Persistent or worsening ear pain;
- High fever, especially in children;
- Fluid drainage from the ear, particularly if it’s thick or discolored;
- Hearing loss that doesn’t improve after the infection subsides;
- Severe dizziness or balance problems;
- Recurrent ear infections within a short period;
- Pain that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter pain relievers.
Coping with Ear Infections: Tips and Tricks
Managing Discomfort During an Ear Infection
Coping with an ear infection can be challenging, but these tips can help make the experience more manageable:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep the body hydrated, which can aid in recovery;
- Rest Well: Get adequate rest to help your body fight off the infection;
- Use a Heating Pad: Apply a warm, not hot, heating pad to the affected ear for pain relief;
- Avoid Noise: Limit exposure to loud noises, which can exacerbate discomfort;
- Follow Medication Instructions: If prescribed antibiotics, take the full course as directed by your healthcare provider;
- Keep the Ear Dry: Avoid swimming or submerging the ear in water until the infection clears;
- Practice Good Hand Hygiene: Prevent the spread of infection by washing hands frequently, especially before and after touching the ear.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve uncovered the intricate world of ear infections as seen through the otoscope. We’ve explored the types of ear infections, the vital role of the otoscope in diagnosis, and the various treatment options available. Remember that early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and preserving your hearing.
FAQs
While the infection itself isn’t contagious, the viruses or bacteria causing it can spread from person to person.
Not necessarily. Earwax helps protect the ear canal, but excessive buildup can increase the risk of infections.
Adults can indeed develop ear infections, although they are more common in children.
Some people find relief from warm olive oil drops, but it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Untreated ear infections can lead to hearing loss, ruptured eardrums, and in severe cases, the infection can spread to nearby tissues.